A Neutrosophic αβγ-Slice Based Reduction Framework for B-Spline Surface Modeling of Kenyir Lake Bathymetry Data
Keywords:
Type-2 neutrosophic set, B-spline surface interpolation, type-reduction, α-slice approximation, bathymetry modeling, Kenyir Lake, interval representation, secondary membership functionAbstract
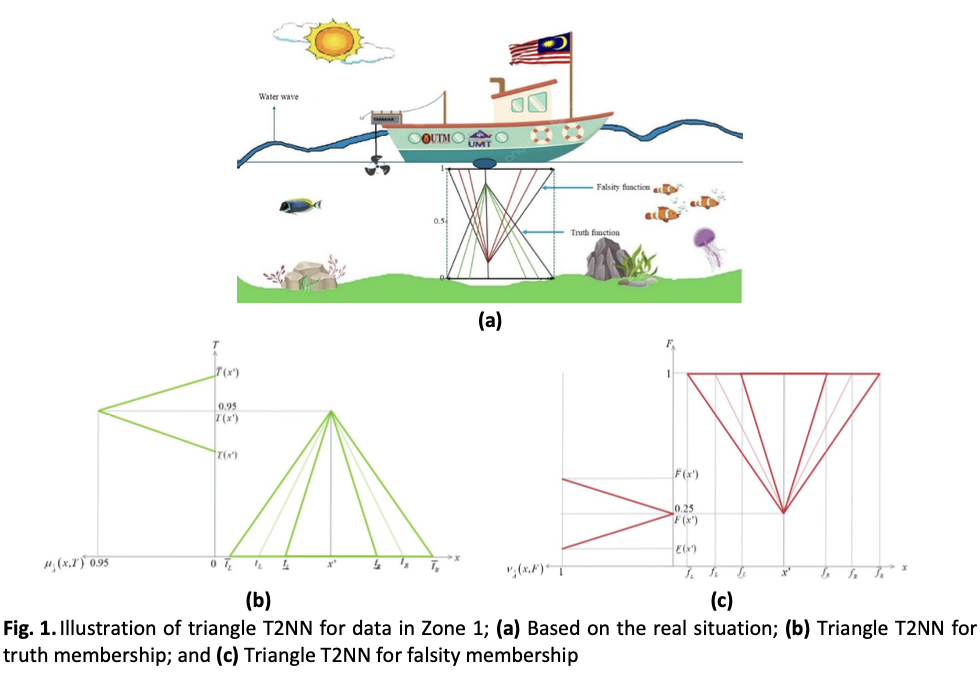
Modeling bathymetric surfaces often involves managing the uncertainty inherent in collected data. Type-2 neutrosophic sets (T2NS) provide a robust mathematical framework to represent this uncertainty, especially when truth, indeterminacy, and falsity values vary over secondary domains. However, the practical interpretation and visualization of type-2 neutrosophic B-spline surface (T2NBsS) models remain computationally challenging due to their complex structure. This research addresses the problem of simplifying T2NBsS interpolation models for real-world applications, particularly in the context of Kenyir Lake bathymetry data. The main objective is to visualize a reduction technique that transforms T2NBsS into a type-1 neutrosophic B-spline surface (T1NBsS) form without significantly losing the accuracy of the information. To achieve this, we propose an α-slice based vertical interval approximation strategy that slices the secondary membership structure at selected α levels to extract interval values of the type-1 triangular neutrosophic set. This method bypasses iterative centroid computation and enables efficient surface reconstruction while preserving essential neutrosophic characteristics. The results confirm that the proposed method effectively bridges the gap between theoretical modeling and practical geospatial interpretation. This framework offers a valuable tool for researchers and engineers dealing with uncertain spatial datasets in environmental and hydrographic domains.