Analytical Study of Velocity and Dispersion Function in Unsteady Non-Newtonian Blood Flow with Chemical Reaction in a Straight Artery
Keywords:
Casson fluid, non-Newtonian, blood flow, Generalized Dispersion Model, chemical reactionAbstract
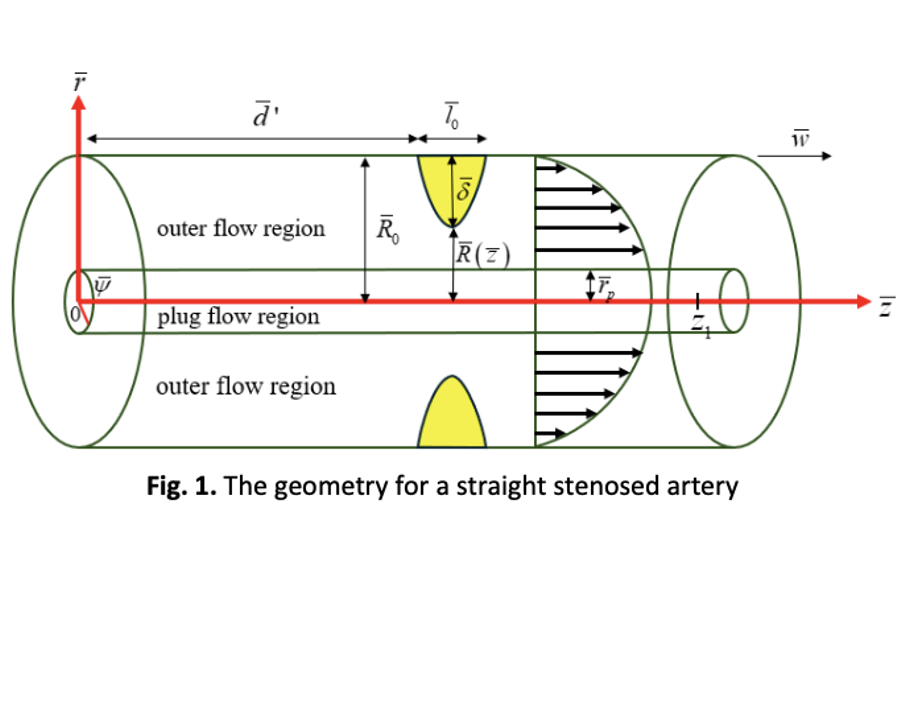
Accurate drug delivery in stenosed arteries is influenced by blood flow dynamics, particularly velocity distribution and solute dispersion. This study investigates unsteady solute transport in a non-Newtonian Casson fluid through a straight artery with symmetric stenosis, emphasizing the effects on velocity and dispersion function. Using the Generalized Dispersion Model (GDM), the governing equations are solved to assess how variations in plug flow region, height of stenosis, length of the stenosed area, length from the origin till the stenosed section and the axial position impacts the blood flow characteristics. Results indicate that the presence of stenosis significantly reduces axial velocity due to increased yield stress, especially near the arterial walls. The dispersion function exhibits a declining trend in these regions, suggesting limited solute spread, whereas higher dispersion is observed at the arterial center. The interplay between yield stress and stenosis geometry contributes to complex dispersion behavior, offering insights into convective-diffusive transport under physiological conditions. This analysis enhances understanding of solute dynamics in stenosed vessels, with implications for optimizing targeted drug delivery strategies.